In this last post of a series dedicated to Microsoft Sustainability Manager, I want to underline the features available which will help Sustainability Managers to take reduction actions in order to have a positive impact regarding carbon emission within the company.
After having ingesting activity data and run calculations to generate emissions in Greenhouse gases, the analysis done in the Analytics with the embedded Power BI reports will rise some topics to focus on for carbon efforts.
As a remainder, here is the list of all posts regarding this topic :
That is where scorecards and goals will be very useful for stakeholders. It’s now time to create a scorecard.
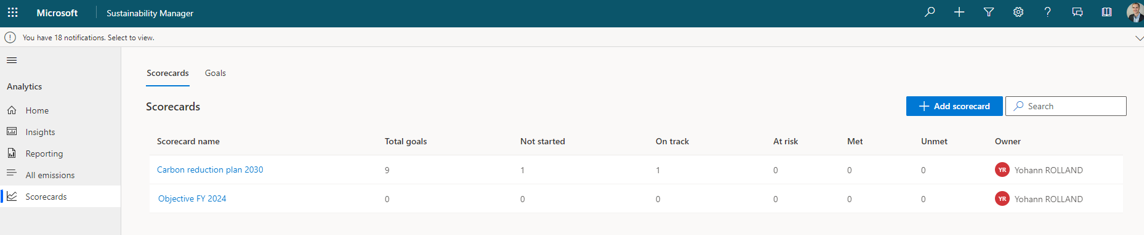
A scorecard is a way to gather all individual objectives called goals. For instance you can setup a scorecard per facility, per fiscal year, or whatever has a meaning.
From a scorecard, you can add as many goals as you want.
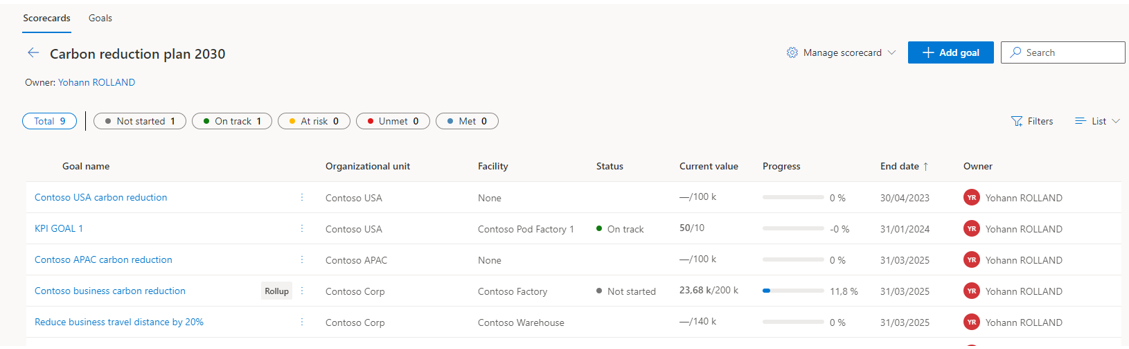
Choosing “Add a goal” to define a new one. You will have different options here.
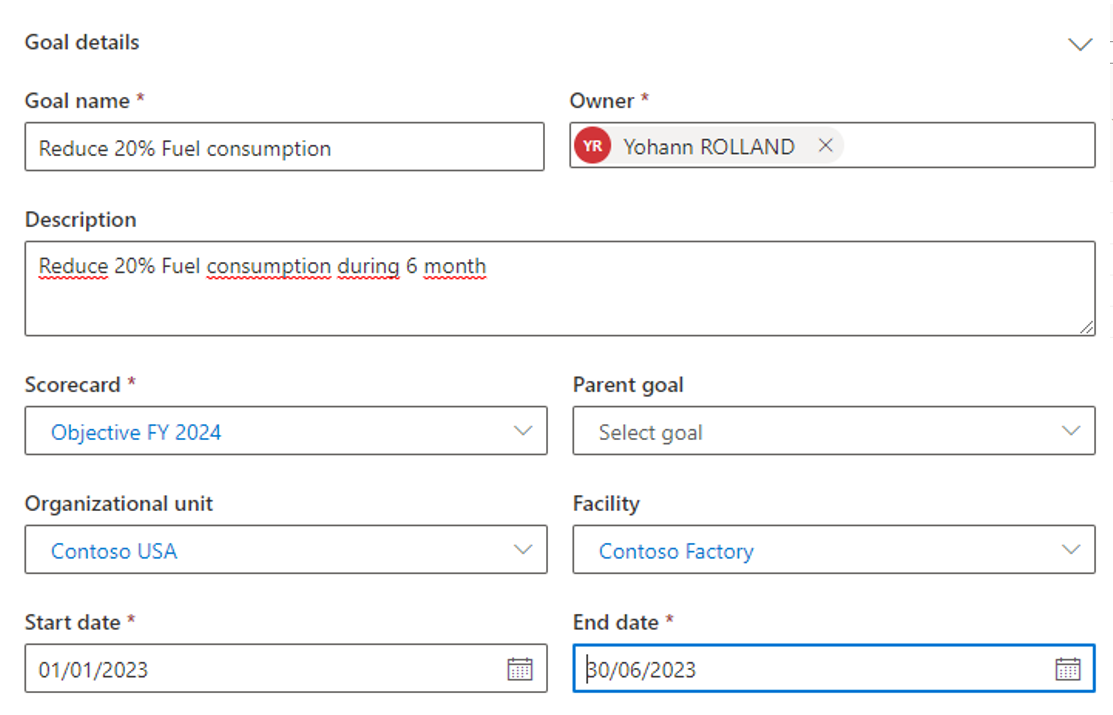
What is mandatory are : linked scorecard, start and end date (one month, one year…), name and owner, but you can define a description, a parent goal, organizational unit and Facility.
The starting value is important as it’s the value of the current goal for the entire period (see Start and End date) before taking reduction efforts.
The Source of target value is the target value for this goal.
You will have to setup the unit of measure of the current goal which is also mandatory.
Any source of current or target value can be filled manually or connected through connectors or Activity Data / Emissions calculated.
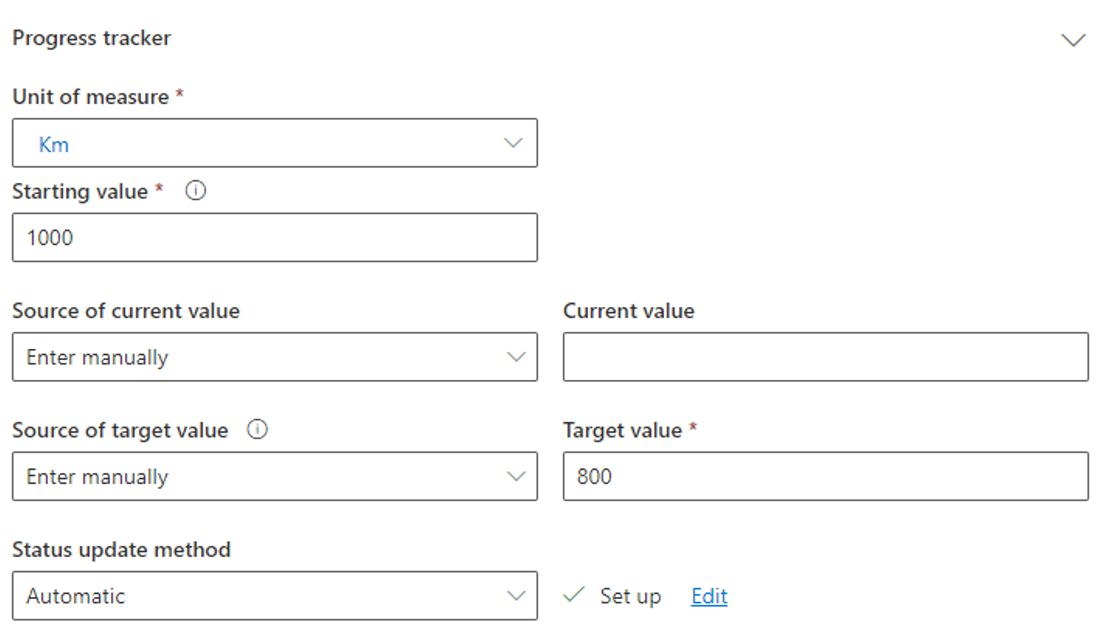
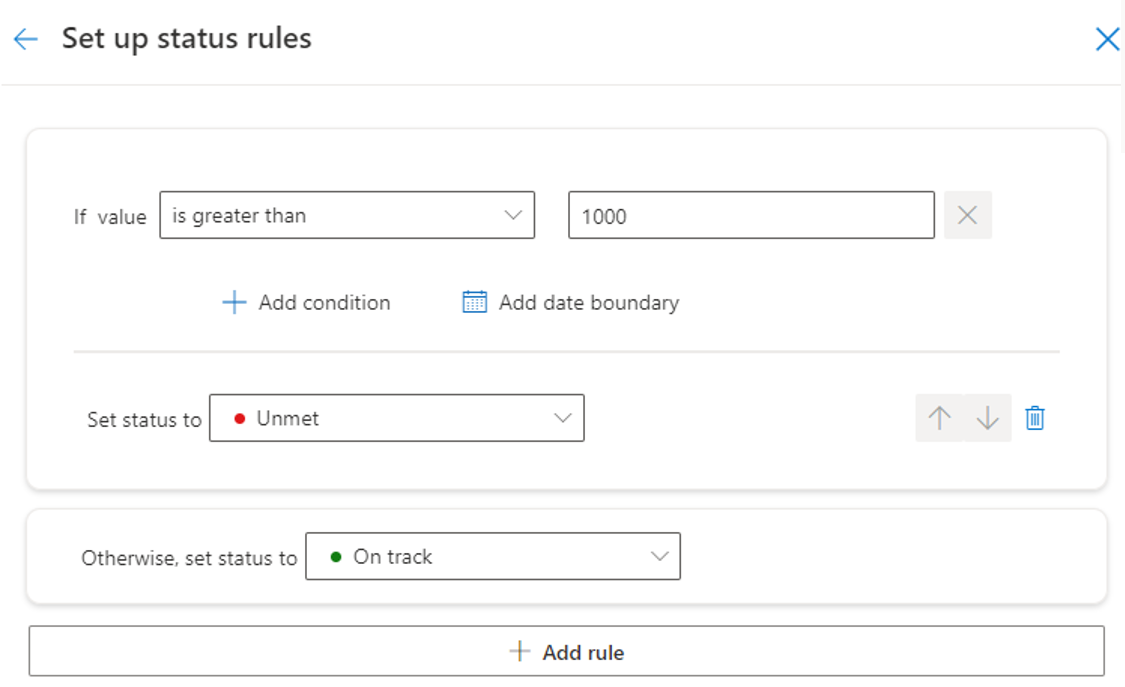
There is 5 different status for each goal. The status update method allows you to define the rule to update them.
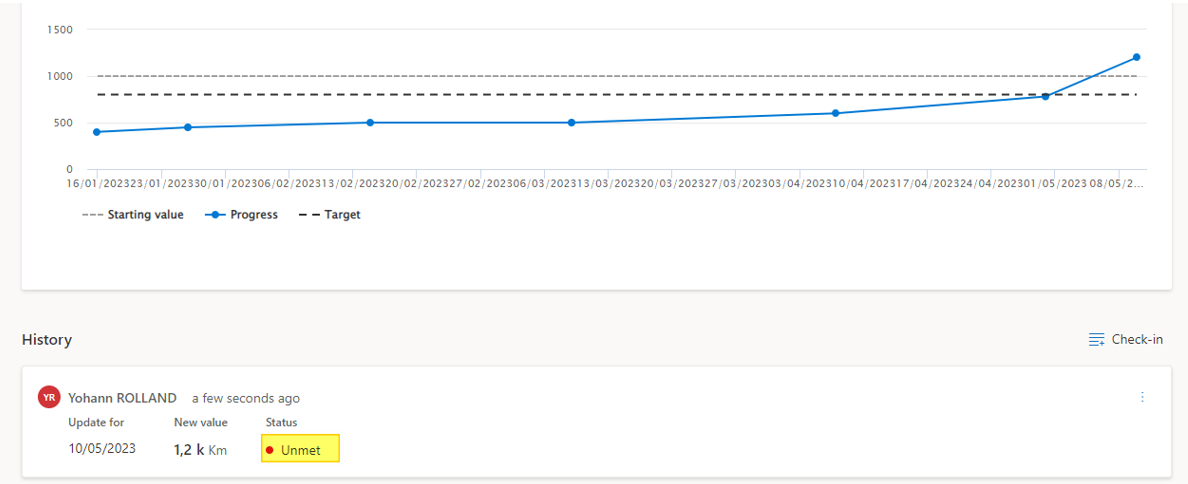
Here is an example of updating the status to unmet.
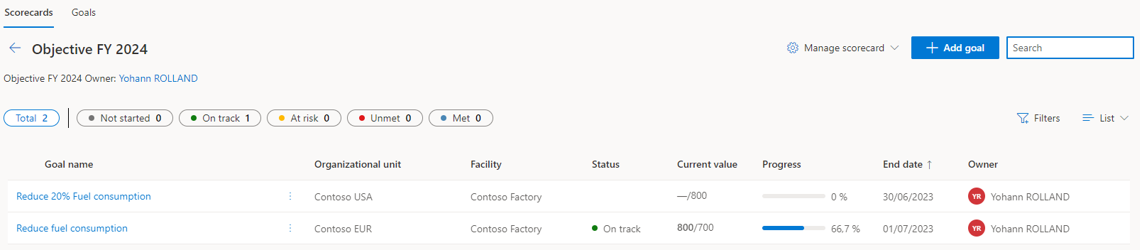
When the setup is done, you will find the list of goals available under the scorecard.
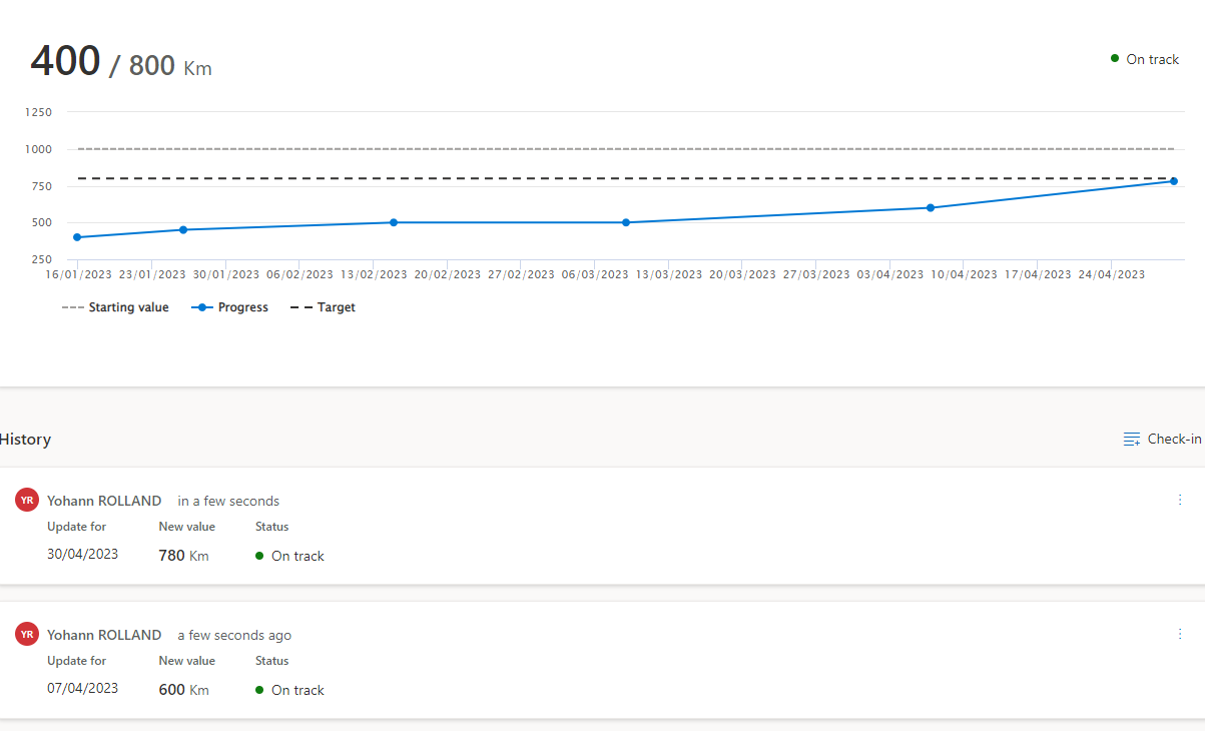
As you can see below, you will find the current status, the name and organizational unit /facility associated with important fields such as the start and end date, the current value (the second value is the target value of the goal). It’s also possible to filter this view.
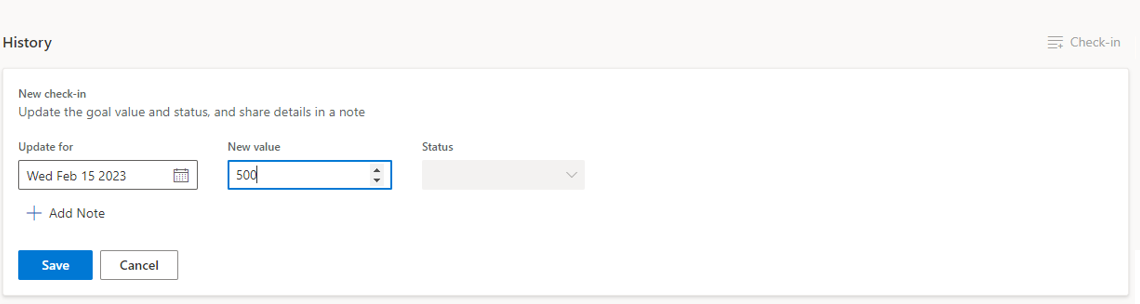
On each goal you can update the current value by adding a new check-in (date, current value, new status if manual update).
The graphical view displays the progress, the starting value and the target value.
In the current example, I have unmet the goal as the value is above 1000. The status has been here updated automatically.
I have not fully digged the out of the box functionalities, but I hope it will give you a first help to start on this new tool.
We can expect new features according to the roadmap of Microsoft Sustainability Manager such as new Scope 3 categories, and a full ESG integration.
Yohann

